What is a flexible solar panel?
Why Not Use Flexible Solar Panel? Cons
When considering the use of flexible solar panels, it is essential to understand their potential limitations and challenges. Here are some key drawbacks that might affect the overall performance and long-term viability of flexible solar panels:
- Cost Issue: The manufacturing process of flexible solar panels involves more advanced technology and materials, which directly leads to higher production costs. This high cost makes flexible solar panels relatively expensive in the market, which may not be an economically viable choice for individuals or organizations with limited budgets. Despite their installation flexibility and lightweight nature, the high initial investment could deter some users.
- Shorter Lifespan: Compared to rigid solar panels, flexible solar panels have a shorter lifespan, which is an important consideration. Rigid panels can last from 25 to 40 years with proper maintenance, while flexible panels typically last only between 5 to 15 years. This shorter lifespan means that they may need to be replaced more frequently, thereby increasing long-term maintenance costs.
- Susceptibility to Damage: Although the bendability of flexible solar panels provides convenience for installation on irregular or curved surfaces, this characteristic also makes them more susceptible to physical damage during use. Frequent bending can lead to cracks in the solar cells, and when installed on rooftops or mobile vehicles, the softer plastic surface can be scratched by external sharp objects such as branches, further affecting the efficiency and lifespan of the cells.
- Overheating Issue: Because flexible solar panels are often in close contact with the installation surface, lacking the air gap that helps cool rigid panels, this design reduces the space for heat dissipation, which can lead to overheating in hot weather. Overheating not only reduces the efficiency of the batteries but can also accelerate material aging, shortening the overall lifespan of the panel.
- Efficiency Problem: Flexible solar panels generally have lower efficiency, which is particularly critical for applications where space is limited but energy demands are high. The main reason for this low efficiency is the thin-film technology used in these panels, which allows for flexibility and lightness but cannot match the solar conversion efficiency of traditional silicon-based panels. In solar panels, conversion efficiency is a key performance indicator, with flexible panels typically ranging from 10% to 17% efficiency, while rigid panels can exceed 20%.
- Durability and Reliability: While flexible solar panels have advantages in installation flexibility and lightweight, their durability and reliability are significantly lower, which cannot be overlooked. Flexible panels are more susceptible to environmental factors such as temperature changes, mechanical damage, and UV radiation. These factors accelerate material aging, reducing the lifespan and performance of the batteries. Additionally, due to their thinner and softer nature, flexible panels are more likely to be damaged in extreme weather conditions, such as storms or hail.
- Shorter Warranty Period: Compared to rigid solar panels, flexible solar panels usually offer shorter warranty periods. This is particularly important in terms of budgeting and long-term maintenance costs. Rigid solar panels, due to their structural and material stability, typically offer warranties lasting 25 years or longer, while flexible solar panels often do not exceed a 5-year warranty. This shorter warranty period reflects the uncertainty about their durability and the potential need for more frequent replacements.
- Heat Tolerance: The heat tolerance of flexible solar panels is relatively low, which is also a concern. In high-temperature environments, the performance of flexible panels may significantly decrease due to thermal effects. High temperatures not only affect the efficiency of the cells but can also cause structural damage to the materials, thereby impacting the overall functionality and lifespan of the panel.
Why Choose Flexible Solar Panel? Pros
According to Allied Market Research’s Flexible Solar Panels Market report, the global flexible solar panels market size is expected to reach USD 914.07 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2021 to 2030.
Why do flexible solar panels maintain such a high market share despite having so many significant disadvantages over traditional glass-laminated solar panels? Flexible solar panels offer several distinct advantages that make them suitable for specific applications where conventional panels may not be feasible. Their adaptability, ease of use, and portability make them ideal for many users looking to utilize solar energy in innovative and efficient ways.
- Installation Versatility: Flexible solar panels can be installed on a variety of surfaces where rigid panels won’t fit. This includes curved surfaces such as boat decks, RV roofs, and even uneven surfaces on certain types of buildings or temporary facilities. Their ability to adapt to different shapes and angles provides greater flexibility in design and application.
- Lightweight and Portable: One of the most significant benefits of flexible solar panels is their light weight. This makes them ideal for weight-conscious applications such as lightweight structures, mobile units, or portable solar solutions. The reduced weight also minimizes stress on mounting surfaces and structures, making installation easier and safer.
- Easy to Transport and Install: The flexibility and light weight of these panels make them easy to transport and install, often requiring less hardware and labor than rigid panels. This reduces overall installation costs and enables solar power installations in remote or hard-to-reach locations.
- Aesthetic Integration: Flexible solar panels have a low-profile appearance that is less noticeable than traditional panels. They can blend seamlessly with the architectural elements of a building or vehicle, providing renewable energy while maintaining aesthetic integrity.
- Durability in Specific Conditions: While flexible solar panels are typically less durable than rigid panels, the latest flexible solar panels are designed to withstand potential environmental stresses such as wind and corrosion, especially in marine and coastal environments. Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes have improved the resilience and longevity of flexible solar panels.
- Ideal for temporary or mobile applications: Due to their ease of installation and removal, flexible solar panels are ideal for temporary setups such as pop-up events, temporary camps, and emergency power solutions. They can be easily rolled up and transported to provide versatile power wherever it’s needed.
- Reduced installation complexity: Flexible solar panels can be affixed directly to a surface, eliminating the need for bulky mounting systems, which reduces installation complexity and cost. This also reduces the time required for installation, making it possible to implement solar solutions quickly.
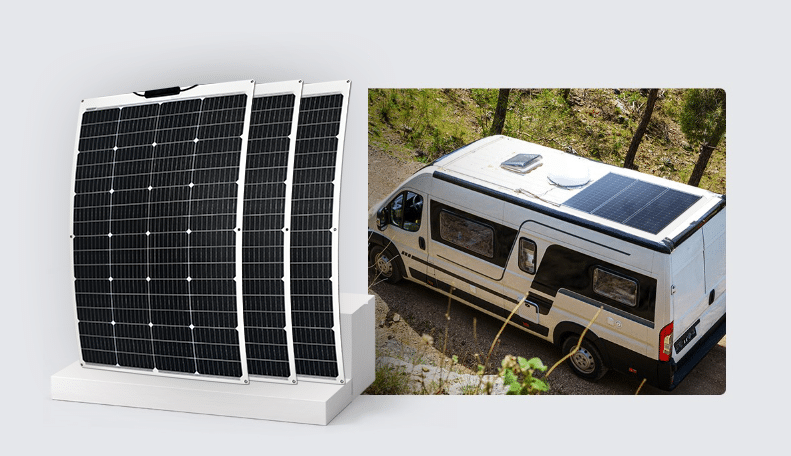
Flexible Solar Power Panel PA621
Lightweight Design
The PA621 Flexible Solar Power Panel weighs only 4.4 kg/m², significantly reducing the burden of installation and transportation while maintaining structural integrity and durability.
High Conversion Efficiency
By utilizing high-efficiency monocrystalline silicon solar cells, the PA621 achieves an impressive conversion efficiency of 22.7%, greatly enhancing energy collection efficiency.
Exclusive Cooling Technology
A unique back sheet material design with a thermal conductivity of only 0.2 W/(m·K) optimizes performance in high-temperature environments and effectively prevents overheating issues.
Enhanced Durability
The PA621 features an enhanced physical structure design that improves the battery’s vibration resistance and structural strength, addressing the issue of cell micro-cracks and extending its lifespan, making it more suitable for harsh environments.
Quick Installation: The simple installation process takes just 15 minutes, making the PA621 an ideal choice for a variety of installation scenarios.
FAQ: Flexible vs. Rigid Solar Panels
What are the differences between flexible and rigid solar panels?
Flexible solar panels are made from materials that allow them to bend and flex, typically up to a 30-degree curve. They are lightweight and can be installed on surfaces that are not flat. Rigid solar panels, on the other hand, are built on a solid frame and are much sturdier. They are usually made with glass and aluminum, making them heavier and requiring a stable, flat surface for installation.
What are the advantages of flexible solar panels compared to rigid solar panels?
Flexible solar panels offer several advantages:
- Versatility: They can be installed on curved surfaces such as RV roofs, boats, and non-flat architectural structures.
- Lightweight: Their light construction reduces stress on surfaces where they are installed and makes them ideal for portable solar solutions.
- Ease of Installation: Due to their flexibility and lighter weight, they can be easier and quicker to install, often requiring less mounting equipment.
What are the disadvantages of flexible solar panels compared to rigid solar panels?
While flexible solar panels are versatile, they also have some drawbacks:
- Durability: They are generally less durable than rigid panels. Their flexibility can make them more susceptible to damage from environmental factors like strong winds or debris.
- Efficiency: They usually have lower efficiency rates compared to rigid panels. This is partly due to the materials used and their thinner construction.
- Heat Tolerance: Flexible panels can suffer from higher heat degradation over time, which might affect their performance and longevity.
What is the lifespan of flexible solar panels?
The lifespan of flexible solar panels generally ranges from 10 to 15 years, which is shorter than the 25 to 30 years typical of rigid panels. The actual lifespan can vary based on the quality of the panel, the environment in which it is used, and how well it is maintained.
Do flexible solar panels overheat?
Flexible solar panels can overheat, especially if they are installed on very hot surfaces or in environments with high ambient temperatures. Overheating can affect their efficiency and durability. However, some newer models are designed with improved heat dissipation technologies to mitigate this issue.







